How to find printed books
How to find printed books
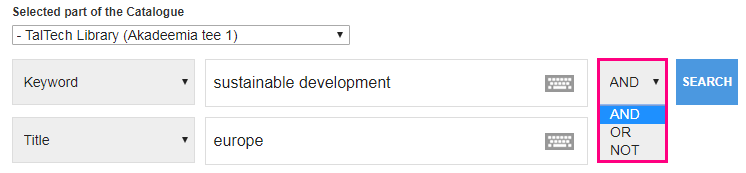
Extended search
By using extended search you can combine several search terms with Boolean operators AND, OR, NOT, NEAR.
Use AND when you need to narrow your results. Using operator AND means that all your search terms must be presented in the resulting records.
Use OR to broaden your results. Using operator OR means that either one or both of your search terms can be presented in the resulting records.
Use NOT to narrow your results. Using operator NOT means that only the first of your search terms can be presented in the resulting records.
For example – keyword: sustainable development AND title: europe
By extended search, you can also limit your search with language, material type, publication year, etc.
NB! Many books are available also as e-books, notice the buttons.
Proximity operators
NEAR and ONEAR
Some databases allow you to use proximity operators, but most do not. The proximity operator allow you to make a search that where you can determine on which distance is one word from another. You can also create a query where search terms appear in the same paragraph or sentence.
Use the proximity operator, when query including the AND operator leads to too many results and these do not match the topic.
Depending on the database proximity operator NEAR will have a different notation.
Proximity operator NEAR can be used in the simple search of the following databases:
- Web of Science climate NEAR/10 change
- Scopus (water OR vinegar OR wine) w/5 (oil OR yogurt)
- IEEE Xplore "hybrid electric vehicle" NEAR/15 "plug‐in"
- EBSCOhost Web (tax OR tariff) N5 reform
